* AUTHENTICITY * LOVE * WISDOM * RIGHTEOUSNESS * COURAGE * FREEDOM *

FREEMASONRY
Freemasonry is one of the world's oldest and largest fraternal organizations, tracing its origins back to medieval Europe, particularly to the stonemason guilds who built cathedrals and other structures. Over time, these guilds evolved into more symbolic organizations, where the focus shifted from actual stone-masonry to philosophical and moral teachings. The modern form of Freemasonry began in the late 16th to early 17th centuries in England and Scotland.
Freemasonry is not a religion, though it requires members to believe in a Supreme Being (often referred to as the "Great Architect of the Universe"). The organization itself is non-denominational and welcomes men of various faiths, as long as they uphold the belief in a higher power. Freemasonry does not promote any specific religion or religious doctrine, but rather encourages members to follow their own faith and moral compass.
Freemasons gather in local units called lodges, which meet regularly to conduct their activities, rituals, and charitable work. Each lodge is governed by a Master, who is elected by the members. The Grand Lodge is the overarching governing body of Freemasonry in a particular region (such as a country or state) and oversees the lodges within its jurisdiction.
Members of the fraternity often greet each other with a special handshake or gesture, which symbolizes their shared membership. They also have a code of conduct, known as Masonic etiquette, which dictates respectful behavior both within and outside of Masonic meetings.
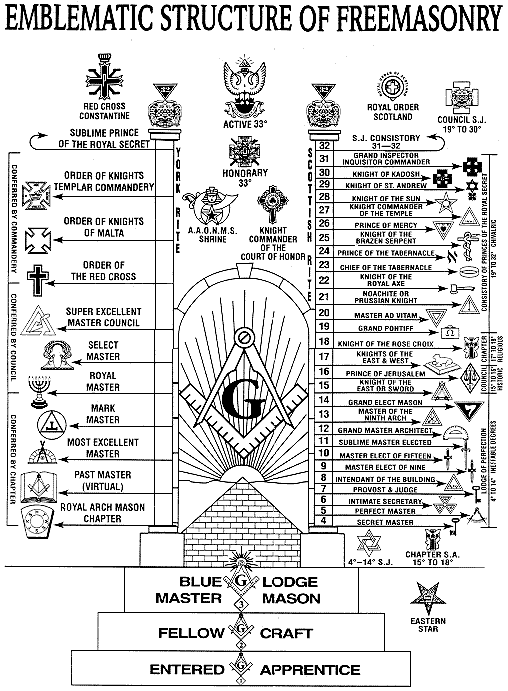
Freemasonry operates in a hierarchical structure with different levels or "degrees" that members pass through. The most common system of degrees is the "Blue Lodge" or "Craft" Masonry, which consists of three main degrees:
-
Entered Apprentice (1st degree): The first step, focusing on initiation and learning the basic principles of the fraternity.
-
Fellowcraft (2nd degree): The intermediate level, with a deeper focus on personal development, education, and the symbolic teachings of Freemasonry.
-
Master Mason (3rd degree): The final degree, signifying full membership and the mastery of Masonic teachings.
Freemasonry is structured around a series of "degrees" that represent a member’s progress in the fraternity. The three main degrees, Entered Apprentice, Fellowcraft, and Master Mason, are part of the "Blue Lodge" system, which is the foundation of Freemasonry.
Beyond the basic three degrees, Masons can advance to further degrees in various systems, each of which offers more elaborate teachings and additional layers of ritual. Two of the most well-known systems are:
-
Scottish Rite: This is one of the most extensive Masonic rites, containing 33 degrees (including the three from the Blue Lodge). It’s known for its intellectual depth and is highly respected within Freemasonry.
-
York Rite: Another system of degrees, which includes the Royal Arch degree and the Knights Templar degrees, focusing on the historical and Christian aspects of Masonic tradition.
Freemasonry has its own specific language and terminology, which might seem obscure to outsiders but has deep meaning for members. Here are some common terms:
-
Brother: A term of address for fellow Masons, signifying the bond of brotherhood.
-
Lodge: The meeting place of Freemasons, where rituals and social activities take place.
-
Master: The leader of a lodge; the title for the presiding officer.
-
Worshipful: An honorific title for the Master of a Lodge (e.g., Worshipful Master).
-
Tyler: A lodge officer responsible for guarding the door and ensuring that only Masons enter the meeting.
Freemasonry is heavily reliant on symbolism and ritual. These rituals, although secret in nature, are deeply ingrained in Masonic culture, and they convey moral lessons through allegory and symbolism. For example, the act of initiation into Freemasonry itself is a symbolic "death" and rebirth. The individual is blindfolded (symbolizing ignorance) and led into the lodge, where they undergo a series of symbolic tests that reflect the journey from darkness (ignorance) to light (knowledge).
Freemasonry is known for its use of symbols, many of which come from the tools of stonemasons. Some of the more common Masonic symbols and their meanings include:
-
The Square and Compass: Represents the importance of morality (the square) and wisdom (the compass). The letter "G" is often placed in the middle, representing both "God" and "Geometry," the latter symbolizing order and structure in the universe.
-
The Plumb Line: Symbolizes uprightness and integrity in one’s actions.
-
The Hourglass: A symbol of the passage of time and a reminder to use one’s time wisely.
-
The Level: Represents equality—reminding Masons that all men are equal in the eyes of the fraternity.
-
The Apron: Masons wear a white lambskin apron during rituals, symbolizing purity, and the reminder to live morally and ethically.
The Illuminati, a secret society founded in the late 18th century, is said to be linked to Freemasonry, with claims that the Illuminati is an offshoot or even an elite faction within Freemasonry itself, whose goals included secularism, enlightenment ideals, and the overthrow of traditional religious and political systems, secretly controls global events and institutions. Some conspiracy theorists believe that the Freemasons and the Illuminati are working together to create a New World Order (NWO), a global government that undermines sovereignty and individual freedoms.
The Freemasons are often accused of being at the heart of a global conspiracy to establish a one-world government, the "New World Order," which would control politics, economics, and society through a shadow network of elites. Many influential figures who are Freemasons are believed to advance globalist agendas, undermining democracy and individual liberty.
Many prominent political figures, judges, police officers, and even military leaders are Freemasons, which gives the organization significant sway over global and national decisions, that Freemasons control key decision-makers to advance their hidden agendas.
Freemasonry subtly influence the media, entertainment, and advertising industries by embedding Masonic symbols, rituals, and codes into movies, television, and advertisements. Many famous figures in Hollywood or the entertainment industry are Freemasons, and that they use their influence to shape public perception. Symbols like the all-seeing eye, the pyramid, or the square and compass (a key Masonic emblem) are often cited as hidden messages in popular culture.
Freemasonry is often said to have descended from the Knights Templar, a medieval Christian military order that was suppressed by the Catholic Church in the 14th century. Freemasons are the modern heirs of the Templars, and that they secretly preserve the Templar’s ancient knowledge and traditions. Masonic rituals are used to preserve the secret knowledge and power once held by the Templar order.
Freemasonry is said to be connected to global financial institutions, with the claim that a Masonic "elite" controls global banking systems.
Freemasons use their influence over financial systems, such as the Rothschild family or central banking institutions, to control economies and enrich themselves at the expense of the general public.
Freemasons are accused of controlling educational institutions, with the intent to shape the minds of future generations toward a particular worldview. Freemasons have control over elite universities or educational boards, promoting curricula that serve the interests of the Masonic order and its global agenda. The Rockefellers controls the public schooling system, as the first 7 years are the formative years to mold the minset of a person. Universities are also the recruitment grounds for potential members through the various fraternities.